We know that online marketing continuously changes, which is why I am trying to envisage what we can expect in 2024 and beyond.
To know what needs to be addressed and executed to promote our websites, we have to understand that the most important thing for search engines is to provide a great user experience and deliver relevant, accurate results fast. This is a search engine’s raison d’etre, upon which their business model has been built to harvest the investment of billions of dollars! This “user experience” goes well beyond simply providing answers to certain questions, and we are not just referring to the search box and everything appearing on the results page, but in particular, to everything that happens after the click. In practice and theory, search results must be accurate, since search engines are indirectly responsible [morally at least] for any unpleasant incidents resulting from a person’s journey from the problem to the solution (stolen money or personal data, virus infection, non-functional or temporarily unavailable websites, undelivered products, delayed flights, rigged elections and so on). This is precisely where the most interesting SEO tasks reside, though not always readily apparent or visible. The job is and shall always be for SEOs to make sure that their “answer” takes the user intent into account, that it is appealing and elegant, trustworthy, certain, adapted to the user’s necessities and possibilities.
In a word – perfect.
Before we check how this SEO “science” and profession has evolved, let’s return for a moment to the SEO definition we wrote a few years back – “control and improvement of ranking criteria which are collectively analyzed by the search algorithm, and lead to a better positioning on results pages”.
Control. Improvement. Therefore – ma-ni-pu-la-tion!
With few exceptions, search engine optimization has always been an epic battle between spammers and search engines. I say “spammers” because although Google’s most important online promotion rule could not have been formulated any clearer than, “Promote websites as if there were no search engines“, and yet almost no one bears this in mind.
Except for successful SEOs!
Which is why over the years, ranking algorithms, which determine the quality of search results, have evolved exclusively to enhance the user experience.
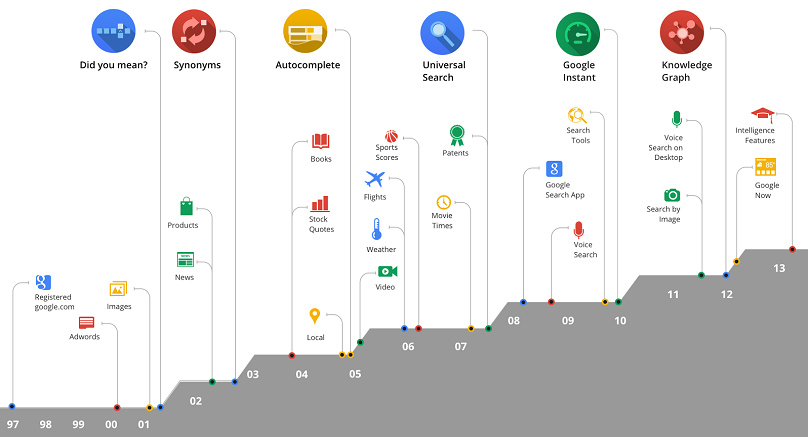
Here are some of the distinct paths user experience improvement efforts have been made upon:
Detection of search intent – adding options such as “Did you mean?”, searches via synonyms and variations, auto-fill suggestions, the Knowledge Graph, and the migration from a system based on key-words and text to one relying on intent, context, meaning, and perception. For instance consider the (Hummingbird algorithm announced in 2013 and RankBrain, launched in 2015).
Indexing quality – mention is made here of the various invisible optimizations intended for scanning and construing the entire Internet, in order to isolate and save in the Index extremely simple, clear and atomic “content items”. This allows associating search queries with qualitative replies and relies upon search advances such as HTML code exhaustive analysis, CSS and Javascript code interpretation, natural language neuro-linguistic processing, analysis of the “feeling” and behavior within SERPs, and more.
Addition of vertical searches – that is, extremely filtered and accurate results when the search intent is crystal clear and narrow in range, such as with images, videos, products, news, books, flights, accommodation, local businesses, weather information, mathematical operations, conversions from one measuring unit to another, sports results, movie recommendations, maps, blogs, invention patents, trends, cooking recipes, etc.
Adoption of new trends, standards and technologies – voice search, sanctions against websites that rely on Flash, priority for small mobile devices (phones and tablets) as opposed to desktop systems / laptops, addition of load speed and SSL/HTTPS-secured connections as ranking criteria, geographic customization using GPS coordinates, priority for multimedia content or appealing presentation versus classic text, Google Instant, etc.
Embedding results directly within SERP – However criminal this may sound, Google aggregates data from various popular and trustworthy sources and presents them directly on results pages as a Direct Answer; which means the creators of this content do not actually receive the traffic, the user remains on the search page. Here are a few practical examples: SSL, Boston, Population of Romania, Manhattan weather, 2024 movies, 100 usd in eur, 2 to the power of 11 etc.
Customization of results – for years search engine workflow has used the following principle: Resolution = Conversation + Anticipation. This makes a lot of sense when you consider that Google attempts to solve problems, not only to provide answers to questions. The perceived “intent” is taken into account, especially if the search query is equivocal. The results are customized based on the user’s tastes and preferences, with the most important customization criteria being:
- geographic (pages with increased local relevance and popularity [country/city/language])
- time-related (content which is currently highly relevant)
- search history (similar searches and preferred results, respectively)
- browsing history (interests)
- social media (content shared by influencers)
- the device (including the operating system and the browser)
- information obtained from other Google products (Chrome, YouTube, Gmail, Calendar, etc.)
Spam control – I have left this chapter to the end since this is where all the magic happens: penalizing websites lacking value and maintaining a clean and safe index. Google has been compelled to develop protection mechanisms to combat and prevent abusive tactics, like an Internet Police of sorts. Some of these preventatives and protections include NoFollow, MayDay, PageLayout, Panda, Penguin, and manual penalties.
Progress over this period has been immense, and I believe the simple lesson we all could learn is that the day will come when search engines will be able to identify user intent and return a solution which is unaffected by spam tactics and poor practices. Engaging in spammy and poor SEO tactics is simply wasteful of time and money, and will not deliver long-term value.
We’ll get to the 2024 promotion stuff in a minute, but don’t you think, we ought to see what mistakes were made up to this point, and avoid repeating them?
Let us not panic so much about 1900-2023… I deliberately chose this period since “SEO is a lifestyle” (my personal slogan since forever).
SEO experts have always been around, since ancient times, and that’s not going to change anytime soon. We are talking about perfectionists, people who pay attention to details and know that in life everything can be optimized. Something can be made faster, more compact, more beautiful, more durable, more elegant, more poetic, more stable, more friendly, more eco-friendly, more pragmatic, calmer… better.
This is why our slogan at SEOlium is:
We believe that in order to take the flight – it’s not enough to copy or imitate something. You also have to be able to dream. In fact, this is how mankind came up with air conditioning, the helicopter, color and sound films, the flight into space, the Ford Mustang, ATMs, the mobile phone, the computer, the internet, fiber optics, the iPod, etc. You think all of these were made by inventors, but let me tell you, they’re all SEO experts!
The biggest SEO mistake during the 1900-2023 period was a lack of vision. Here are a few smaller mistakes, as well, without detailed explanations but with examples:
|
Not having a website [ It’s actually Matt Cutts who said it :-) ]
Non-indexable content, with a number of causes:
|
Black-hat SEO, that is, promotion using methods that manipulate, deceive or are not permissible by search engines. Here are a few examples:
|

|
Before moving on to the next chapter I would like to add one more thing. There is one category of people who always understood what SEO means and how a website should be promoted. I am talking about those who do not believe in miracles but are willing to invest time and effort to achieve results.
Such people believe in genuine value and disregard any other system that takes the “path of least resistance”, they have never been alarmed by search engines, since each progressive advance helped their websites gain more exposure on result pages. Algorithms have never been against them, as a significant portion of the so-called “SEO experts” seem to believe. On the contrary – they have patiently waited for search algorithms to improve and fully reimburse their efforts to perhaps make the world a better place.
This chapter may be of interest to three types of people:
- those who have just searched for “SEO in 2024”, believe that SEO changes from one year to the next and wish to know what Google has in store for them. Well, here’s a short summary: SEO principles do not change. Anything can be optimized!
- those who believe that SEO will die. I’m sorry to disappoint you guys, but SEO has always been and will always be around since it’s not so much about optimizing websites as it is about optimizing “experiences”.
- SEO experts, businessmen and, the curious folks. No summary or brilliant ideas for you. Only an exercise in imagination.
I should mention that, while writing the first 2 chapters, I felt like an unprepared high school student facing exit exams. Well, it couldn’t have been any other way – the Internet is barely 27 years old, and I was about to tell you how things would pan out 32 years from now?! While contemplating, I suddenly remembered a situation which happened quite some time ago, but gave me the guts to continue:
Years went by and many men lost their head; the sultan got old but had not lost hope.
 One day, a strange fellow came to the court saying that he was the only one capable of teaching a donkey how to speak.
One day, a strange fellow came to the court saying that he was the only one capable of teaching a donkey how to speak.
– Your grace, the beast is not human, I shall teach it how to speak, but it will take me 10 years!
– As many as it takes! replied the sultan enthusiastically.
– I shall need food, clothes, a nice home and other things for the donkey, plus ten thousand gold coins every year, the fellow said.
– Anything! the sultan said and ordered that all of these be provided.
Once they came to an agreement – the man took the donkey with him and went home, to a faraway village. When he got there, everyone had words with him:
– What did you do that for? Do you really have a death wish? to which our fellow replied untroubled:
– Well… A lot can happen in ten years… The sultan, the donkey or I myself may kick the bucket…
Right, shall we now teach the donkey how to speak?
I would like to commence with an observation.
Everything that was made over the centuries: castles, planes, revolutions, phones, songs and oranges – was done for comfort. In essence, any action or lack of action stems from self-interest that may convert into comfort. Physiological, psychological, financial, domestic, emotional or visual comfort. Right away or later on.
Let’s start with the idea that if there are issues, solutions will be found. If opportunities exist, providers will emerge, and come what may, comfort shall prevail.
Let’s begin with the conceptual issues affecting “real life” in various parts of the blue balloon
- pollution (air, water, soil)
- global warming
- overpopulation and housing costs
- slow rides, traffic lights or jams
- work exploitation and discomfort
- monopoly markets
- society division
- energy conservation
- health
- poverty
- malnutrition
- accidents
- terrorism
- waiting lines
- gadget vulnerability :)
- jealousy

And a few issues affecting the “online”
- information abundance and filtering
- personal data security and information volatility
- mass misinformation, manipulation, fear or panic
- testing products prior to purchasing them
- long delivery times
- currency conversions, money transfer fees and other particularities pertaining to payments and foreign currencies (by the way, here’s a great resource if you need SPAC stocks analyses and data)
- e-commerce fraud and other types of cybercrimes
- participants’ real identity
- spam
Fortunately – we know for a fact that some of these issues will be solved by
- smart and economic homes
- robots (household, agricultural, industrial)
- driverless cars (and other independent means of transportation)
- drones (manufacturer-to-consumer deliveries, fire extinction, extractions, etc.)
- 3D printers (housing, urban furniture, roads, etc.)
- Personal assistants fitted with artificial intelligence (for solutions, not just answers)
- chat-bots for customer, as well as sales support
And some life aspects that will not change by 2050
- the laws of Physics
- teleportation
- taxes
Now, close your eyes and let’s dream about life in 2050
Free internet – Fixed and mobile telephony will disappear. Same goes for television and other cable services. The lost tribes of the Amazon will have access to satellite internet, but will not be aware of it. The situation will not make internet providers or mobile carriers too happy, unlike people though.
An IP for everyone – People will only be able to access the internet using their personal IP address; spam activities will slow down, and some prison sentences will be replaced by applying certain sanctions to the criminal’s IP. Passports, driving licenses, IDs or cash are going to disappear as people will always have their full identity on them, including their medical history, preferences, bank account etc. (an RFID capsule injected above the left collarbone).
Universal income and work-life balance – Many lines of work (farmers, taxi drivers, factory workers, pharmacists, deliverymen, etc.) will be replaced by robots. People used to spend their days hunting, farming and herding for food and warmth. Work has always been a solution rooted in necessity and not something done because it was pleasant. However in 2050, food will be cheap, and certain products may even be free. The law of Conservation of Energy will finally be applied in agriculture (watch Matt Damon’s movie The Martian). No longer will people be consumed by the necessity of making a living, instead they will have the time, support, and encouragement to go forward to discover and pursue their talents. A minimum income will be provided by governments of major countries such as China and the United States, creating harmony between obligations and satisfaction. France will be the first country to officially cancel the business day, and the maximum number of weekly working hours will be -40 =))
The twilight of banks and cash; the age of digital currencies and online wallets – I am mostly referring to physical contact: trips to bank counters or cash payments in grocery stores. Financial and crediting institutions will still exist, but their services will be different from those available today and will be solely held online. The markets will democratize, home deliveries will be free of charge; online stores, payment, and currency conversion fees will lead towards the need for a single currency. The cryptocurrency model will prove non-functional and virtual money will, therefore, be regulated.

Medical advancements – Let’s start with the “corrective” medicine, to be partially replaced by the “preventive” one; naturally, surgeons will still be required, but I am not convinced they won’t be robots. I simply can’t imagine “family physicians” or diagnosticians still practicing medicine. Lab tests will be periodically processed by an internal device, all data will be uploaded into the cloud and solutions will come out of the collective memory, experience, and intelligence.
Moreover, we’re going to have devices capable of projecting thoughts, sensations, and emotions (something connected to the retina or directly hooked up into the brain) or being controlled by the power of thought (mouse, keyboard and microphone commanded by the brain?). Transmitting smells, tastes and states across the internet will be possible. The human body will act as a source of energy for gadgets.
High-performance batteries, energy efficiency and billions of gadgets – I will admit that science is not my strong suit, but the theory seems much simpler to me than what happens in practice. For instance, you fetch a few atoms [OK, OK – electrons] and move them from one spot to another, et voila! You have electricity :)) But why has the supply of clean, environmentally-friendly, and cheap electrical power that can be taken anywhere it is needed taken so long to develop?!
The invention of a compact, high-performance battery will change all aspects of life.
“Online” regulations – The internet, barely in its infancy, is seen by all sorts of wannabees as a vulnerable and appropriate place for dubious activities. A virtual Wild West where the law of the ‘malware gun’ rules and the laws of “real life” can be avoided. Cybercriminals rejoice at the lack of a virtual policeman who will pursue them and bring them to a just punishment for theft, fraud, slander, discrimination, personal attacks, fear and harassment, spam, blackmail, manipulation or other types of disrespectful and unpleasant behavior. This is due to change.
Let us see how SEO will change by 2050
Do you remember me saying that “Everything in life is about SEO. Except SEO. SEO is about power.”? Well, I wasn’t joking. SEO doesn’t reside in optimizing websites, but rather in optimizing “experiences”.
SEO is about analyzing the demand and creating supply, which is why we can say it’s been around since ancient times and will exist forever.
Some even say that SEO is the oldest profession; older even than “the oldest profession”.
Solutions instead of answers – simple needs (services, products or information) will be fulfilled by personal assistants similar to the one provided by Google. Plane tickets, hotel reservations, car rentals, 2nd degree equations, sports results, food and beverages, the population of Mars, etc.
A new wave of “standardization” (Schema.org) will allow search engines to understand information even better.
A protocol will be invented, allowing direct transactions between computing machines (online shopping carried out by robots) and in this way, the “human element” in sales will gradually disappear.
A few large marketplaces will emerge (vertical search engines such as Amazon, AliExpress, ThemeForest, Expedia, Booking, etc.) and all suppliers will add their products and services, accompanied by relevant information such as specifications, prices, terms and conditions, etc. The reviews shall have integrity and reliability, while personal assistants will be able to select the best offer based on available information and the boss’ preferences. Risk and liability will be borne by the marketplace, the end user always coming first; disputes and litigation will be settled between the marketplace and the supplier without involving the user, even if the complaint originates from them.
Large information providers may eventually segregate from “the rest of the world” and tag their content with no-index to discourage search engines from displaying direct answers. But perhaps we’ll also see an acceptable “compensation” method, for instance, renting a controlled amount of advertising space or payment per direct answer API request.
There will be an abundance of commercial content, probably produced by artificial intelligence and with a perfect optimization score. Establishing relationships will more important than ever, in contrast with today’s link-building.
Search engine manipulation and black-hat tactics will go down. SEO experts (and their bosses) will focus on optimizing product and service quality, pricing and customer experience.
Out of the Four Ps of Marketing – only two will remain!
Ultra-personalized experiences – each person will enjoy a “predilection index”, augmented by Big Data projections and refined in time by means of machine learning methods. Essentially, your emotions are constantly going to train your very own little Panda pet. The estimated “satisfaction” score will be the most important SEO ranking factor.

Real, virtual and multidimensional experiences – technological and scientific advances will keep the same fast pace, which is why we may soon find ourselves browsing more than just 2D websites on Google Chrome.
We’ll switch from Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and HyperText Markup Language (HTML) to HyperState Transfer Protocol (HSTP) and HyperState Markup Language (HSML). Web pages’ source code will describe, in great detail, the visitors’ multidimensional experience, whereas the browser will convert it into virtual or augmented reality, while inducing sensations or states: smell, taste, temperature, humidity, brightness etc.
The classic trip to the store will be replaced by a virtual trip. Same goes for testing products prior to purchasing them. The first businesses to embrace the new technologies will be those operating in the fields of HoReCa (hotel, retail, café), tourism and real estate.
I’d like you to take a brief closer look at the trends over the past 5 years (Google Trends).
Our experience is counter-intuitive: the market does not grow exponentially or even linearly, as one might have expected; on the contrary – we actually feel that interest in SEO is dropping. The SEO-related queries’ search volume is declining and the sudden burst in 2016 is nothing but an improvement in data collection.
So our biggest prediction is, in fact, quite small – the “online” will be the same in 2024 as it was in 2023 or the years before (namely 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019, 2018, and so on). Same budgets, same optimization techniques, tasks, work methods or paradigms. What do SEO, websites, and people have in common? They change, only… slowly. However, same doesn’t apply to search engines, so let’s see what they have in store for us.
Web safety has always been important to people, but not a priority when compromise came with slower page loading times. Beforehand, computers were larger and faultier while the internet was small and slow. Nowadays, however, devices are smaller and effective, whereas the internet is vast and fast. Technologies (fiber optics; wi-fi, 4g, smartphones, tablets, AppStore, the cloud, drones, etc.) have opened new possibilities and changed the way users behave. The fear of using a credit card for online shopping is slowly fading away, and people are reasonably expecting to maintain their comfort, privacy, and safety while surfing the web.
For these reasons, safe connections (HTTPS) have evolved from a slightly negative SEO factor (indirectly, due to the reduced speed) to an important SEO signal. Moreover, as of 2017, even browsers such as Chrome warn us when the pages we surf on are unsafe. This will certainly be a trend in 2024, therefore install that SSL certificate at once, mkey?! The upside is that this is a simple sitewide optimization, i.e. it helps each individual webpage. There may be only a 1% bonus at stake, but believe me, when you rank 2nd or 3rd for a search phrase this “boost” may help.
One aspect is that SSL is more important when personal data protection (people’s identity, log-in data, bank data, etc.) is imperative, as is the case with online stores, e-mail, social networks, etc. and less important when the landing pages are purely informative and no exchange of personal data takes place.
Traditionally, the SEO recommendation for meta descriptions was 150-160 characters (156), however, in late 2017 Google started displaying larger search results snippets, of up to 320-400 characters. This is quite lovely for website promoters in several respects:
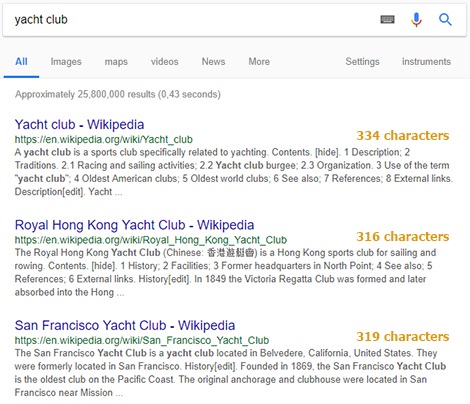
- longer descriptions provide more SERP real estate, vital for presenting distinctive features of the page people land on, therefore doing a better job at convincing them to click on the search result (you may offer guarantees, promotions, discounts, a phone number, etc.).
- a Google search result may now take up to 7 lines (as opposed to 3-4 for many years until now): the URL address, the title, star-reviews and 3-4 lines of meta description, instead of the previous 2. This means that only the top 3-4 results (on a desktop, 1-2 results on mobile devices) will be visible above the fold and the user will have to scroll down for the rest. Ranking #1 or #2 for your favorite keywords is more important than ever.
- longer descriptions also mean more search keywords, which in turn can lead to a significant advantage for long tail queries: the words will be highlighted in bold and CTR may increase.
It’s important to mention that the absence of a description is also acceptable, in which case Google will auto-generate something relevant for the user, according to the search query and the actual text on the page.
So, instead of “sweating” on a bad meta description, how about saving a few bytes and leaving it blank?! :)
It’s not clear why Google went for these changes, but let me invite you for a glass of conspiracy theory: longer descriptions will damage Bing’s SERPs [should someone actually use Bing :)))]. Nooo, we don’t think that, but, hey – when search intent is purely informational, descriptions will be so informative that users will no longer click on search results. We can expect the traffic of news websites, Wikipedia, Quora and others to drop dramatically.

To understand what I’m talking about and to convince you that it is true, pick up your phone right now and launch the Google search app (usually available straight from the home screen, if you know how to use a smartphone), Chrome browser or www.google.com in any browser (laptop / desktop / tablet). Tap the microphone icon then ask calmly and clearly: “BestBuy working hours”, “food delivery” or “is Empire State Building open?” Results are impressive. They actually work as rightfully should.
Careful though, this functionality is highly addictive!
Voice search was launched several years ago, but only gained popularity with the mass adoption of smartphones, 4g connections and, more than anything else, Google’s breakthroughs in natural language processing. Which leads us to the idea that, as of 2024, pages serving long tail queries well should gain superior exposure.
Until now, out of laziness, people were generally Googling short and vague phrases that sometimes failed to “give away” the actual problem or intent. Consequently, to drive sales, websites needed to optimize and rank well for all user intents (short and long tail keywords), even if it meant [indirectly] paying for a lot of traffic they would end up partially being unable to monetize. Because people just didn’t search using queries like “custom platinum engagement rings in New York City”, did they? So if you wanted to sell – you had to rank for “rings”, “engagement rings” or “custom rings”. To catch your favored fish – you needed to catch all fish first. SEO used to be a game for Ivy League players, but, luckily, 2024 is leveling the playing field, which means excellent opportunities for niche websites.
In 2015, Google stated that in case of mobile queries – pages providing a pleasant and optimized experience will have priority. “Mobilegeddon” was only the first step, but now most searches already occur on smartphones and tablets, and in late 2016 Google announced their intention to set up a primary, mobile-friendly index and a secondary one, for desktop computers only. Naturally, all the information “leaked” at conferences relate to politics and rhetoric. We won’t buy for a second there are two distinct databases, but this statement is an even clearer signal that from now on, websites optimized for mobile experiences will be boosted. Normally, if they were to build an index for each usability criterion, they would have one for fast websites and another for slow ones, an index for websites with https:// and one for those without it, an index for websites infected with malware and one for the healthy ones, and so on.
Traditionally, SEO experts (and even Google themselves) have taught businessmen that, in order to rank well one has to create content and links to it. Valuable, friendly and appealing content + good, relevant and trustworthy links.
This approach generally works well, but it does have a number of limitations and disadvantages:
- it urges people to build backlinks, when it is, in fact, Google’s job to find solutions needed to better understand the relevance and importance of pages. Online businesses ought to invest time and effort into developing products, services, content, etc., without obsessing over links, as J. R. R. Tolkien brilliantly described in his book The Lord of the Links:
– “We wants it, we needs it. Must have the precious. They stole it from us. Sneaky little hobbitses. Wicked, tricksy, false!”
Let’s face it, the situation where you don’t care about SEO and only think about the user experience (ideal content) is simply not an option. Because you may end up waiting for years, and better Google ranks may never turn up. Whereas link-building actually works, which is why everyone is so obsessed with them, whether they admit it or not! - it creates unequal conditions for content creators, namely, it benefits large brands. We shall take the example of a domain name registrar and hosting provider, let’s say: GoDaddy, HostGator, Bluehost or any other. It would be enough for them to issue a press release, launch a new product, do something fun, buy another company or simply change their name for links to start pouring. Has their quality of service changed? No. Will they rank higher in Google? You bet! So what should a smaller company (which often has better customer support, increased security, smarter hosting plans etc.) do to match this situation?
- it leaves the door open for spammers. Creating good content is easy. First, you get your values straight and then you simply create it! Or, if you’re a spammer – you can even copy it from somewhere, but make sure to change a few bits and bobs here and there. Google won’t mind, because what’s important to Google, rather than promoting genuinely good content, is, in fact, to have enough “evidence” that your content is good and uniquely valuable. There is an entire industry working on manipulating backlink signals on the web, and sadly, that industry is called SEO.
- an epic battle between huge budgets and great ideas: links can also be purchased. Everyone does it. And those who don’t – have their listings on the second page, further down. It’s all right to have ideas but having a ton of money is fantastic. Google preaches that payment for “votes of confidence” is an immoral an unfair practice, which increases the risk of a penalty. But let me ask you this – why wouldn’t a company pay for a couple of promotional articles if it helps them increase their exposure? Seems like a fair trade to me. I mean… you want an endorsement, you want to lend someone else’s popularity, you want customers and dream to get rich? Then be a good lad and pay!
- it encourages flattery, nepotism and influence peddling. If you are a notorious person (president, famous writer, TV star, blogger, actor, etc.), it’s easy to channel the audience into producing links. This occurs in a natural manner, much like the case of big brands, but this exposure does not necessarily mean a higher value or remarkable qualities in a particular field. Imagine Ellen DeGeneres opening a chain of pizzerias nationwide. I bet she would leave the Domino’s in the dust overnight! And if you’re not an influencer, you can always pay or cozy up to one.

It follows that, in order to rank better, you have to be obsessed with links, a leading brand, a spammer, have a lot of money or many influential friends. But don’t be upset, all right? The online realm resembles real life with the survival of the fittest, and Charlie Darwin wins!
Perhaps, at some point, artificial intelligence (together with Big Data) will settle these “inequities” for good and manage to accurately estimate the quality of webpages. But for the moment, Google does not have a better solution than analyzing links, and yet progress is being made in that respect as well:
- priority for pages with a higher concentration of accurate and verified information
- treating online mentions as “votes of confidence”, even without a link
- analysis of online reputation and “sentiments” towards brands
It is essential that in 2024 and beyond, you look after the online perception of your brand. Great content and links still remain important, but you should know that relevance, authority and notoriety are also computed based on factors such as online linkless mentions and citations. And maybe even those on TV, radio, books, written press, billboards and other offline sources.
There are also other benefits besides SEO, to having a brand that is known and loved by internet users – it may increase your website’s click-through rate even when it sits further down on search results pages. Furthermore, a trustworthy brand may influence the decision to purchase, and then, even a low website traffic may generate spectacular sales because the brand fuels conversions so well.
Theoretically, search engines should not favor video content over traditional text; however since everyone owning a mobile phone can also shoot a video for YouTube – video content will be omnipresent in 2024. However, the greatest challenge will be to filter information. This is simpler with text as you open the document, instantly realize it’s not what it should be, and you’re out. The reason is that text can be structured, and the main ideas can be highlighted with larger fonts, colored, written in bold, underlined, enhanced with interactive elements like QR codes, etc.
With videos things are more complicated: you first have to wait for it to load and then watch the entire video, which is often a massive waste of time when it lacks any interesting ideas. But, as videos are conceived for speed most producers have yet to invest sufficient time, skill, and resources to make them truly high-quality assets, something that applies especially to amateurs. In the commercial environment the necessary resources, talent, and budgets are much bigger (script, equipment, director, actors, editing, etc.), which will inevitably separate the wheat from the chaff.
I have one thing to ask of you: do not contribute to the dilution of quality in the online environment. Produce content only if you actually have something to say and it will be useful, and not because it’s convenient or trendy.
It’s common knowledge that paid ads do not directly influence organic positions in Google. An indirect effect is when paid traffic generates new organic signals, such as shares on social networks or mentions on blogs, forums, and other websites. The reason why I added this chapter is the relatively low cost in many countries besides USA, Canada, UK, Germany and few others. We ourselves are from Romania and this article was initially written in Romanian and then translated. Later on, our friend Karl Hindle was kind enough to further translate it from regular English into native speaker English. Let’s not deviate from the subject though – AdWords, as a marketing channel, is yet to be harnessed, and businessmen are gradually “waking up”, so I assume it’s fair to say that in 2024 we’ll witness quite an increase in competition. Naturally, in tech-savvy niches such as e-commerce, SaaS, or online services (air tickets, hotel reservations, translations, food delivery), the competition was always huge, but from now on even more niches are going to use Google ads, which have the following advantages:
- pay today – sell today (thus, tests are fairly cheap)
- confidence that visitors are looking to buy (or are at least interested in the product/service)
- total control over the budget (you may set a daily or monthly spending limit)
- option to turn entire campaigns or individual ads on and off (it’s also possible to deliver ads depending on user’s location, language, time, keywords, device, etc.)
- possibility to only target visitors who previously engaged with the website (or even bought something)
As with Google AdWords – outstanding performances in social networks don’t influence Google ranks directly, either. Still – you need to be there. For several reasons.
- Albeit people used to watch a lot of TV, today everyone “wastes” a good amount of their time on Social Media. Some even – day and night. In this day and age, not having a Facebook profile makes you look suspicious. If you want to sell, you need to get in front of people, and for that, a plethora of tools are available to you: paid ads, “company” pages, interest groups, etc.
- Certain [potential] customers wish to get in touch with you in real time, not on the phone, but via instant text messages, i.e. chat and messenger apps. For questions not covered by the website, for details about products/services, for support or for a million other reasons.
- The “subscription” option, that is, you can build a community around the brand, which can be monetized in various ways.
- There is a nice democracy about social networks, where people can recommend your business quite easily, by simply tagging your page in any post. Traditionally, only influencers with blogs were able to recommend you through links in their articles, whereas now everything moves to Social Media.
- In the past, any search for products or services started in Google, whereas now, and especially in the future, everything takes place in Social Media. Search engines will probably still be used mainly for “informational queries”, but nothing compares to a suggestion from a trusted friend, followed by a conversation reflecting their experience with a brand, no? Looking for a wedding photographer? Or a plumber? A car wash? Well, ask around on Facebook! You’re not only going to receive a list of options, but also the pros and cons of each.
Search engines aspire to create ideal user experiences or at least limit the number of unpleasant situations. This paradigm has not changed in recent years and won’t change in the future. What did change, however, is today’s immense computing power, the colossal amount of information and storage capacity. But now we also have machine learning and artificial intelligence to make sense of it all. Search results will be ultra-personalized and it’s more important than ever to make sure that “satisfaction” signals sent by internet users are favorable to your brand.
There is even an invention patented by Google on this topic. In a nutshell, it’s all about collecting a few biometric parameters (body temperature, heart rate, blinking rate, facial skin color etc.) for every search that occurs in the universe, and using predictive models to compute “satisfaction scores” for each search result, depending on the query and the specific search intent. Thus, in time, the system would learn from itself and produce better and better results for a user or a group of users. In other words, link-based metrics are going down and user experience parameters are going up :)
This may sound a bit complicated, but let me rephrase this: Google will pay attention to your body’s reactions and provide better results by filtering out unsatisfactory pages which cause adverse reactions. I’m using the future tense since I don’t really believe that everything mentioned there has already come into effect, but the trend is clear – we will migrate from search engines towards personal assistants, and the results will be tailored depending on increasingly personal and intimate factors.
Current methods of analyzing user behavior in SERPs (including pogo-sticking), which the SEO community has grown accustomed to and accepted, will continue but evolve and refine further. Still, I should mention here that there are major conceptual differences between the way people surf the web using a laptop/desktop and a smartphone/tablet. Search engines are fully entitled to put more “trust” in signals acquired from mobile devices (phones in particular). The reason is a simple one: the “operating” speed (the user’s productivity on the whole) is much lower in case of mobile phones (small screen, no keyboard or mouse, slower loading speed, less effective browsers, lower-tier processor and RAM memory, etc.). To save time, users are thought to be more considered and more responsible in their actions as a consequence.
Is this idea borne out by real-world data?
Let’s press pause and see what happens both on the pages with Google results, as well as after the click:
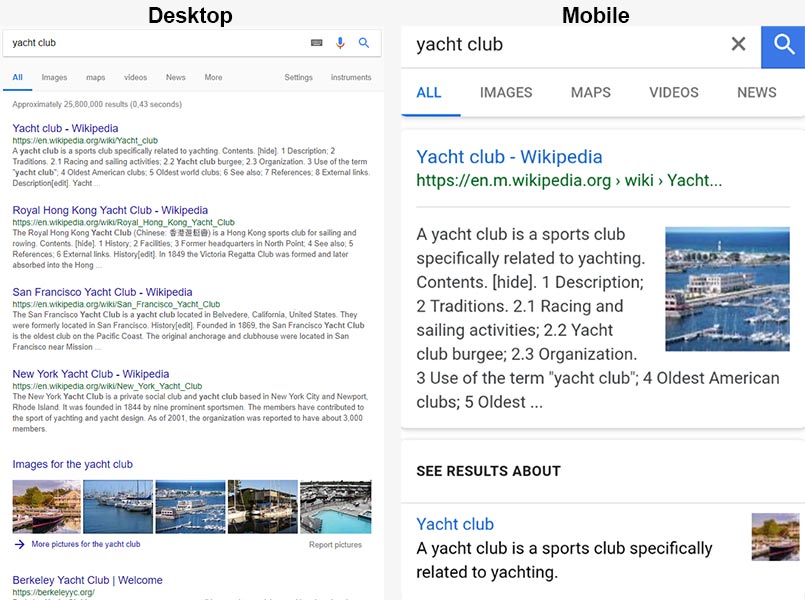
| Analyzed criterion | Smartphone and tablet | Desktop and laptop |
|---|---|---|
| Number of visible results on screen | 2-3 | 6-7 |
| Number of scrolls required for a full SERP | 6-7 | 1 |
| Possibility to open a result in a new tab | low | high |
| Results opened concurrently (usually) | 1 | as many as desired (3-6-10) |
| Seconds to discard a bad result | it depends. 10? 20? | 2-3 |
| Need for optimized (responsive) pages | yes | no |
It follows that a mobile user consumes information at a slower pace, and therefore they will think twice before clicking on a result. Furthermore, when they return to the SERPs, we know something went wrong or they need additional information. And here’s another interesting fact – on mobile phones, Google will be able to confidently calculate the time it takes the user to analyze each search result snippet, especially now that meta descriptions are going to be four lines long. This is impossible in case of full HD desktop screens since 6-7 results are displayed at once. I should also mention that these signals may prove impossible to use in practice, if there is too much “noise”, but for me at least they are clear – if it takes someone 3-4 seconds to analyze a Google result without clicking on it, they have deemed it unfit.