The first and foremost rule in search engine optimization is to offer value, but that is subject to feelings and emotions, hence – it’s always biased. In order to rank well within search engines – you have to provide clear signals that your pages are better than those of your competitors. There are a lot of strategies, tactics and best practices of how to achieve this, but the most important thing you can do is – optimize your content, make sure that everything you own and control is simply excellent. Also, remember that search engines will rank the most important of the most relevant pages. This means that, for a search query, they will first pick up a set of relevant pages and then display them in result pages according to their importance and notoriety.
On-page SEO is all about Creating or Enhancing relevancy signals for a webpage with respect to the search query. Having some experience in optimizing and promoting websites, we were able to deduce few rules that are essential and that helped us to prioritize our work process and increase our results. We hope these rules will help you too.
Before you start writing any piece of content (including title, meta description, image name etc.), you should know which problem you’re trying to solve, that is – what are people really looking for and which expressions have most search volume. You should also take the competition into account and choose the perfect balance between the most searched keywords and those with less competition.
You can do this research using plenty of tools, but the most popular ones are offered by Google (Search, Analytics, Webmaster Tools, AdWords, Trends etc.).
When analyzing the competition – start by googling for the super-keyword and pay attention to their title, meta description, URLs and headlines and then make sure to create better versions. It is of utmost importance to have great URLs, titles and descriptions, as these are the things that make a search engine result snippet.
Referring to keywords location, remember:
The usage of keywords variation is less riskier (because of “over-optimization” penalties). It will help you to cover as much of the semantic field as possible (more long-tail keywords). Also, it’s good to know that long terms are better than short terms (it would be easier to rank for the super-keyword if we used it everywhere)
With the above in mind, it is important to prioritize keywords (based on their estimated search volume).
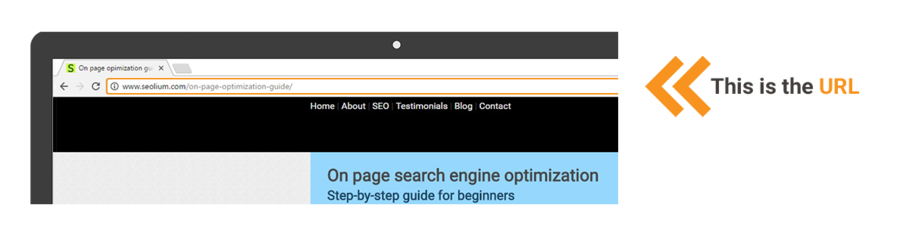
The URL address should describe as closely as possible what the page is about. Users should be able to understand whether the page will fulfill their needs without loading it in their browsers. The URL address suffix (the last part, not including the domain name or parent folders) should be the shortest summary of the page. The URL address prefix (domain name + parent folders) should provide context.
Try to meet the following requirements:
|
|
As a conclusion, we can deduce the following rule:
URL (the Uniform Resource Locator) is an address to a resource on the Internet. This element is important for On page optimization.
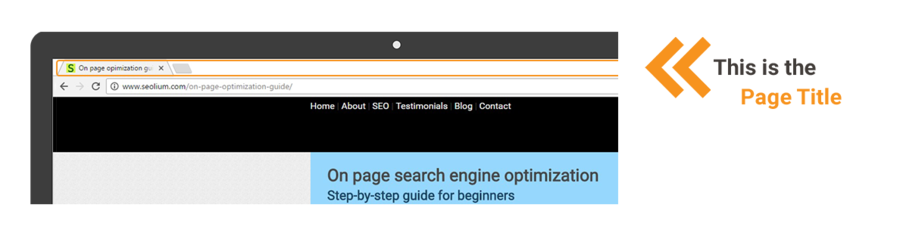
Your title tag appears at the top of the browser and as the headline in search engine result snippets. Social networks also use it as part of the post when someone shares that URL. For these reasons it has both a huge SEO value (it’s one of the most important ranking factors), and a “clickability” value (it serves as an incentive for people to click). You should try to find the perfect balance between excellent SEO and excellent user-friendliness.
Some tips:
|
|
Considering the above tips, remember the next rule:
Title tags are the document definitions, that you can see in various places around the web, including the tab in your web browser. That elements and are used to tell search engines and visitors what any given page on your site is about.
It should be concise, reflecting the content of the page, attractive and memorable for users.
Usually they are implemented as HTML H1, H2… H6 tags, but in fact nowadays search engines are getting better and better at interpreting CSS and Javascript, so headings can really be implemented as anything. It’s a classic scenario when size matters.
These are emphasized text pieces (titles, subtitles, etc.) which show human visitors and search engines the most important “takeaways”.
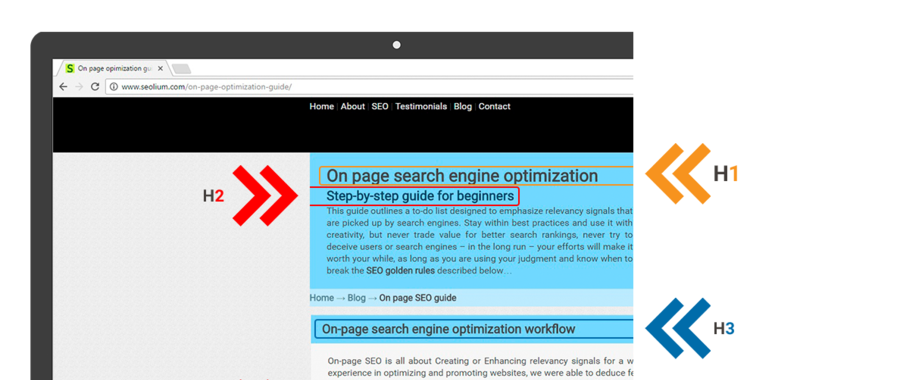
Spiders pay a great deal of attention to the words used in headings, that’s why they should always accurately describe the content below.
The H1 tag (the biggest headline) ,b>should appear at the top-center of the page and should be the first thing people see when they land on it. It should be tailored as a “synonym” (instead of the same text) of the title tag, hence – include the super keyword, or some close variation. There is no limitation to the length, but they should not be too long and should usually fit inside one or two lines.
Some tips: Headlines should clearly communicate the subject of the page they are introducing.
Remember that the page headlines are another reflection of your content.
The heading should be useful and informative, specific and relevant. Try to think beyond the conventional and make it unique and original.
Meta description is a summary of the page and appears as part of a search result snippet, below the page title. It helps people decide whether to click on your site, or other sites above or below. The key is to experiment until you get satisfying click-through rates.
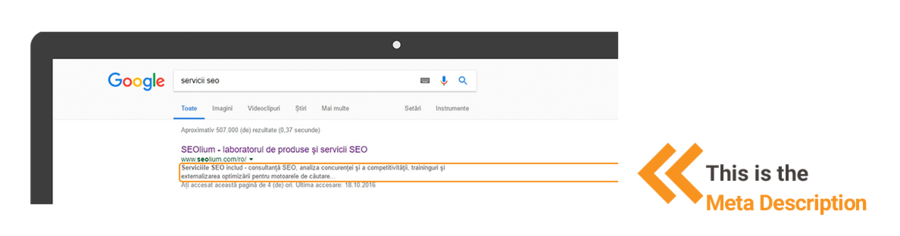
Try to meet following requirements:
|
|
Also note that sometimes it’s a good idea not to write a meta description at all, but this is subject to experiments. When search engines don’t find a description – they will generate one and use that inside the snippet. This is sometimes better because the auto-generated description uses content pieces that contain the search query, thus is relevant and compelling to the user. It’s important to understand that search engines don’t use meta description as an SEO ranking factor. At all. It merely serves as an incentive for users to click on this search res ult, and not on others so there’s absolutely no need to stuff it with keywords.
The meta description essence it is reflected by the following rule:
Meta description it is the HTML attribute that provide a brief summary or an explanation of the page content. It is used on search engine result pages (SERPs) to display preview snippets for a given page. Even if it hasn’t a significant role for SEO, it is an important factor of user-friendliness. It should compelling, super-informative and attractive for the visitors.
We can say that content runs the site. Or that content is King. This is what ultimately drives people to the website, keeps them happy, makes them share it and spread the word.
The user searched for something, then reviewed a list of search results, analyzed URLs, titles and meta descriptions etc. then decided to visit your page. Here is when things really get interesting.
One important rule to keep in mind is that a user will spend 2 or 3 seconds to decide if what they searched for is actually here. This is a critical time frame and everything in front of the user should be crafted to ease that decision.
The headline is the first thing they will see. First paragraph is second and only then will they decide whether or not this page is a good fit for their needs. If they bounce back to the search engine result page (“pogo-sticking”) – your rankings will be hurt. If they stay – the content still has to prove itself worthy.

There are no strict rules of how to write great content, but it indeed needs to be great. One thing to remember though – the look and feels should be designed in such a way that the user shouldn’t need to read every single piece of content in order to get the basic ideas. Instead – he or she should just be able to scan the page and easily extract the most important takeaways. You can achieve this by playing with headlines, bolded texts, internal table of contents, ordered or unordered lists of elements, etc. as long as you just need to read these and get the idea.
Here are some tips and tricks:
|
|
We can deduce the following rules:
Obviously, it should be able to stand on its own (valuable and different from other web pages) and easily solve “the problem” (provide information/answers, take action etc.)
Basically, in order to achieve on-page SEO nirvana, you have to design the content in such a way that it will be clear to anyone (both humans and bots) what they are about. The way you can do this is to insert targeted keywords in prominent locations, i.e. – those areas that users are most likely to pay attention to:
Remember that the first paragraph is a key-element that can capture user attention. Make it carefully and think about your potential visitors – what they expect from you? How can you convince them to read the following text and stay on your website?
We know you’ve heard this a hundred times, but if you have interesting, valuable, informative and funny texts, you’ll attract traffic naturally. Everything in SEO is based on this simple truth.
As mentioned above – search engines will first analyze its URL, then the title, headline, description and so on. Optimization is just making sure that these elements are very suggestive and accurately reflect your ranking intentions. Remember that you can always use an SEO checker to assess and assist with the quality of your content.
All pages should have images as they are important in search ranking. They have an opportunity to show up in an image search, but they contribute to regular SEO as well. It’s considered good user experience to have cheerful, good-looking pages and professional graphics can easily add the missing ingredient. Advanced search engines can also interpret texts within images, but it’s not recommended to hide perfectly crawlable keywords inside them. When optimizing, use the most important keywords for the first image, next ones (synonyms, variations) for the second image, long tail keywords for the third and so on.
Image optimization should meet following requirements:
|
|
Links are very important for SEO. It’s considered good user experience to link to other excellent resources the cover the topic further. They are also usually (and should always be) highlighted within the text so they ease the process of scanning through the document.
When optimizing links, consider the following best practices:
|
|
Performance of your website remains and is a strong ranking factor and is something which you need to focus on. Time and time again, Google has confirmed that websites which load faster rank better than those which don’t. In particular, this will become a stronger ranking signal as mobile search ranking. Mobile connections tend to be slower in general, thus website which have not been optimized for performance will tend to load even slower on mobile devices. Speed being a ranking factor makes sense even from a user perspective – a fast, snappy website is a good user experience and the user metrics have now become core at ranking.
Slow websites also tend to increase your bounce rate, which will negatively affect your rankings. If you want to optimize your website for speed, follow this easy (but detailed) guide on CollectiveRay which is sure to make your website load faster.
|
|